FBCSP Toolbox Architecture
This section explains the architecture of the FBCSP toolbox. To facilitate maximum reuse of the code on other datasets, it has been written in a modular structure.
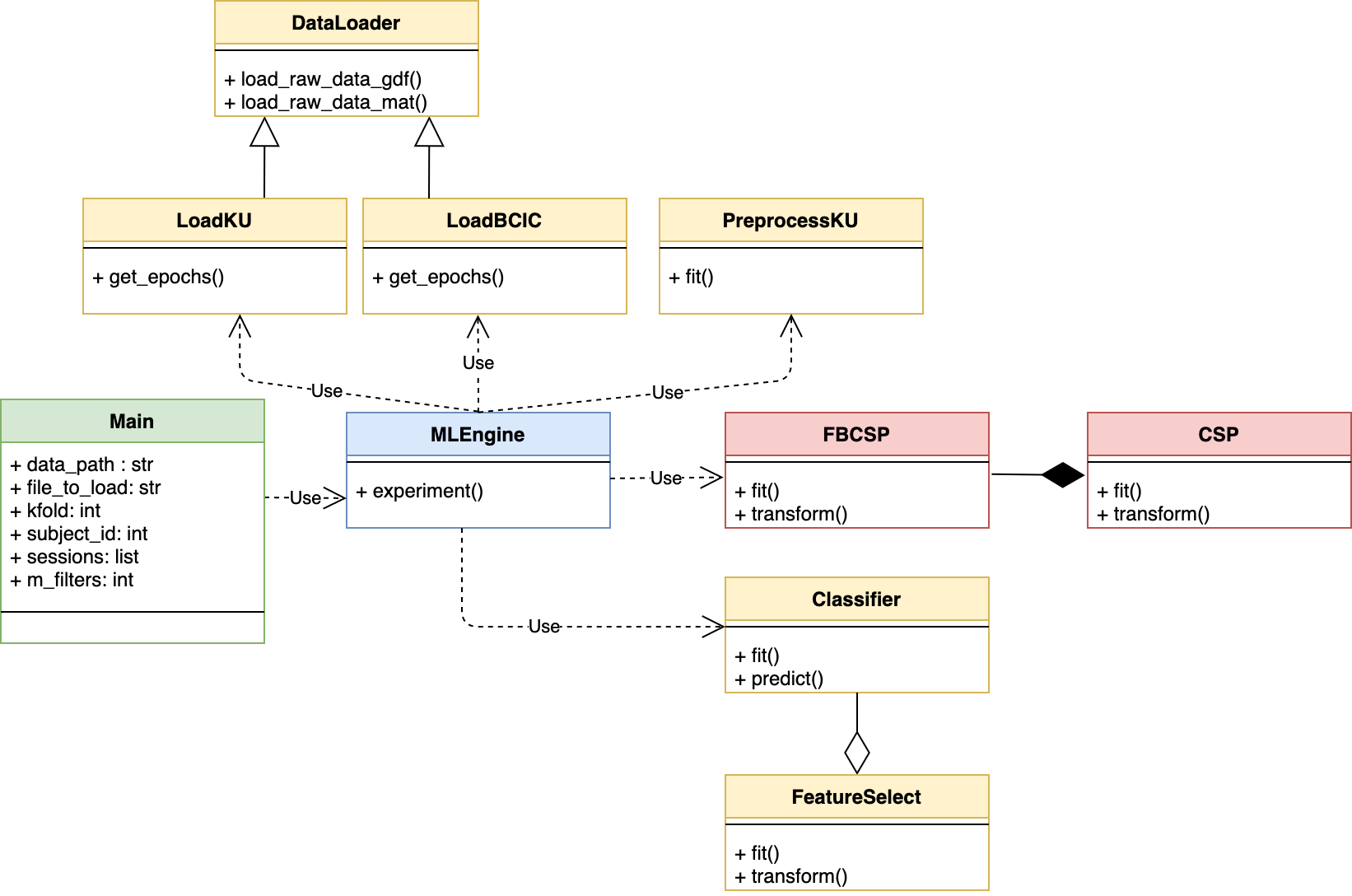
The remainder of this section will provide a higher level overview of the various classes and methods that make up this toolbox along with a UML class diagram.
A manual in a pdf format can be downloaded here for an in-depth, detailed description of the toolbox. A UML class diagram of the toolbox is shown below.
Machine Learning Pipeline
MLEngine
This module serves to integrate the various steps involved in a typical machine learning pipeline for a BCI application. MLEngine.experiment() is the main function that can be used for this purpose. The main components of such a pipeline typically are data loading, preprocessing, splitting the data into training and testing sets, feature extraction, feature selection and classification. To enable maximum reuse of the methods, it is recommended that the data loading functions extract the EEG data into numpy.ndarrays and pass them as outputs for all subsequent signal processing and machine learning. This means that in order to use the other components of this toolbox, data should be arranged as 3D numpy array (trials x channels x time samples) and trial labels should be loaded as a 1D numpy array. The sampling frequency should also be made available to the corresponding classes/methods such as MLEngine.FilterBank. All other dataset specific details should be abstracted away, possibly in other variables/attributes. In order to use this class, an instance can be made in an outer main script by passing the path to the data folder. Subsequent mathods can then be used to invoke data loading, preocessing and classification pipeline.
FilterBank
This class provides the filter bank designed as per the original publications introducing FBCSP. This toolbox uses this class to pre-filter the EEG signals into the various frequency bands which are used to extract FBCSP features. To carry out filtering with a different set of parameters but retaining the same kind of filters, this class can be inherited and its attributes modified as desired. The methods can then be used to carry out filtering of the EEG data.
Loading EEG data
DataLoader
This is the base class that interacts with EEG data files when the (absolute) path to the data folder and filename have been provided. This can the be subclassed to add more functionalities and dataset-specific information for importing and epoching the data. Two exemplary classes have been provided along with this toolbox, namely LoadBCIC and LoadKU, which inherit this base class to load the data from BCI Competition Dataset IV 2a and Korea University, respectively. More methods can be added to this class for intercting with EEG data in other formats.
LoadBCIC
This class inherits the DataLoader and provides added parameters to specifically load and epoch the BCI Competition Dataset IV 2a. All the parameters for loading and epoching data from this dataset have been adopted from here. The function DataLoader.load_raw_data_gdf() is used to import the EEG data from the gdf files provided from the competition organisers. It is to be noted that this function does not download the data. The data needs to be downloaded prior to using this module.
LoadKU
This class inherits the DataLoader and provides added parameters to specifically load the OpenBMI Dataset. This dataset contains three paradigms for BCI, namely, MI, event-related potential (ERP) and steady-state visually evoked potential (SSVEP). This toolbox specifically uses the MI data from this dataset which consists of two classes: left vs right hand MI. The dataset comprises EEG data in .mat files. Epoched data from these files are loaded using the DataLoader.load_raw_data_mat() function. It is to be noted that this function does not download the data. The data needs to be downloaded prior to using this module.
Preprocessing EEG data
PreprocessKU
This class provides a few basic methods to preprocess the data from Korea University. Similar steps may be used for other datasets as well. More functionality can be added here, as needed.
FBCSP
This class is used for carrying out FBCSP as proposed by Ang et al, 2012. There are two methods provided, namely, fit() and tranform() that are used to derive the FBCSP filters and compute the projected features, respectively. This class assumes that the data has already been filtered and arranged in a 4D numpy.ndarray. In order to carry out filtering as per the original settings and design proposed by the authors in Ang et al, 2012, the MLEngine.FilterBank can be used. The FBCSP class invokes the CSP class (in a composition) to get the FBCSP filters (FBCSP.fit()) and compute the FBCSP features (FBCSP.transform()). For details on how CSP is computed, please refer to the documentation of the CSP class.
CSP
This class is used to derive the CSP spatial filters (CSP.fit()) from pre-filtered EEG data for a given pair of classes. Once the filters have been obtained, CSP.transform() can then be invoked to get the CSP filtered features. The FBCSP depends on this class (in a composition). However, this class can also be used independently to compute only the CSP features as well. For example, if a user wishes to compute a differnt variant of CSP, they can then leverage this class.
Classifier
This class can be used to carry out the training and testing for a given classifier. The classifier model must be made in MLEngine.experiment() and passed to this class. The fit() and predict() methods can then be used for training and testing the classifier,respectively. This module also contains the FeatureSelect class which can be used in agregation with the Classifier class in case a feature selection step is desired. However, if this step is not needed, the feature_selection flag can be set to Falseand the methods will not invoke the FeatureSelect class.
FeatureSelect
This class provides options for feature selection, as desired. Running the Classifier with the Classifier.feature_selection flag creates an instance of this class whose methods can then be used for feature selection. Moreover, this class also provides a method for mutual information based individual best feature (MIBIF) selection algorithm that was used in Ang et al, 2012.